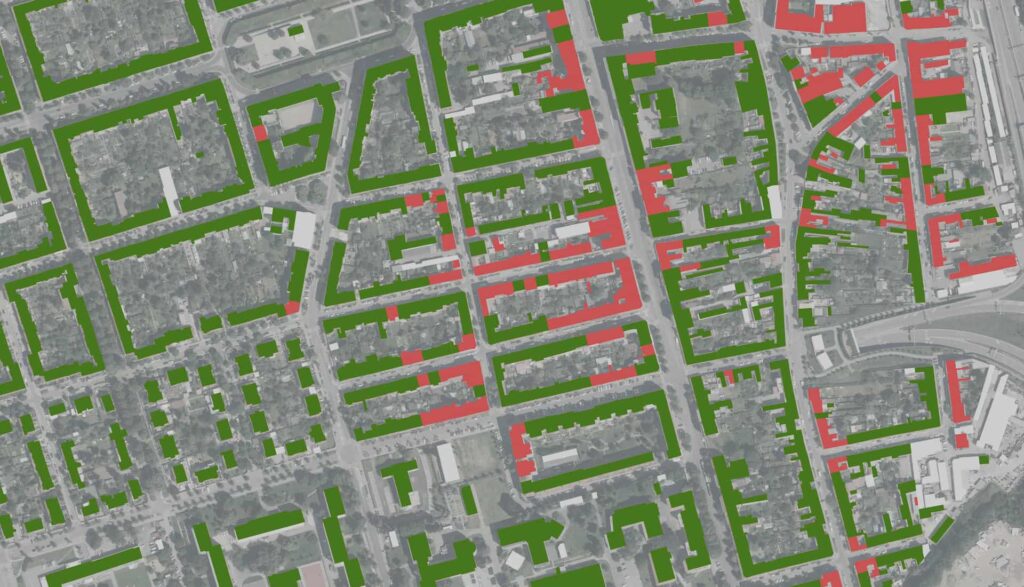
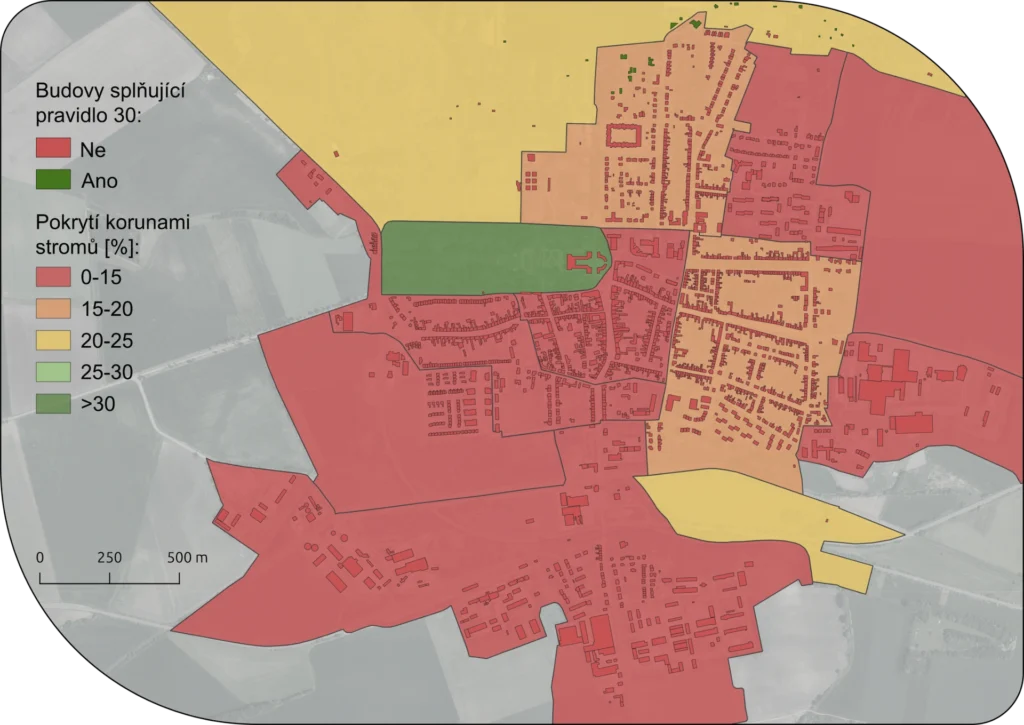
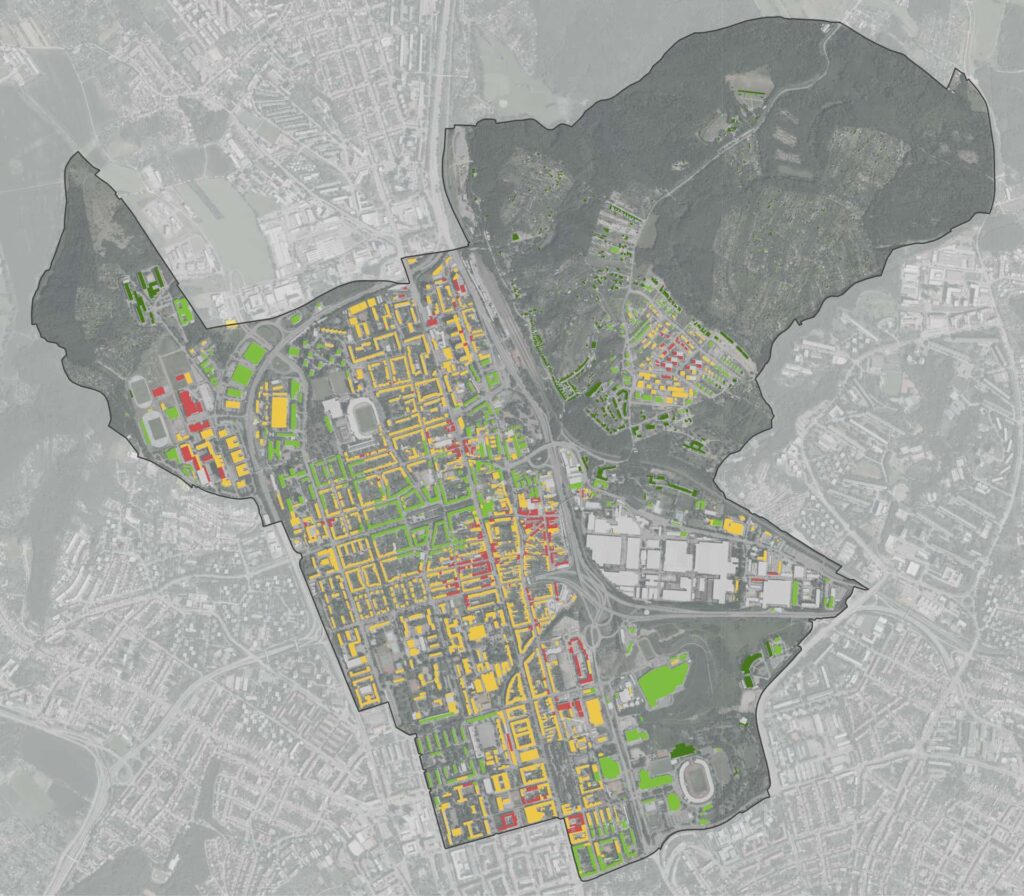
Decarbonization refers to the strategic reduction of carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions through the adoption of cleaner energy sources and improved energy efficiencies. This crucial endeavor targets the mitigation of global warming and climate change by transitioning from fossil fuels to renewable energy sources like wind, solar, and hydroelectric power.
The urgency of decarbonization is underscored by the scientific consensus on climate change, which highlights the profound impact of greenhouse gases (GHGs) on global temperatures. The International Energy Agency (IEA) outlines comprehensive strategies for decarbonization, emphasizing the importance of technological innovation, regulatory policies, and societal shifts towards sustainability. The adoption of electric vehicles, increased energy efficiency in buildings and industry, and the deployment of carbon capture and storage (CCS) technologies are pivotal to these strategies.
Policies play a significant role in facilitating decarbonization. Governments worldwide are implementing carbon pricing mechanisms, such as carbon taxes and cap-and-trade systems, to incentivize the reduction of carbon emissions. Furthermore, international agreements like the Paris Agreement align global efforts, setting ambitious targets for reducing GHGs.
The economic implications of decarbonization are profound but manageable. While transitioning to a low-carbon economy requires substantial investment, it also opens up new opportunities in green technology and sustainable practices. The Global Commission on the Economy and Climate suggests that such a transition could yield economic benefits running into trillions of dollars, spurred by innovations and efficiencies.
For further reading and detailed insights, references such as the International Energy Agency’s reports, the IPCC’s climate change assessments, and studies published by the Global Commission on the Economy and Climate provide invaluable information on the strategies, challenges, and economic impacts associated with decarbonization.
This summary provides a foundation for understanding the vital processes and policies that drive decarbonization, a key to mitigating climate change impacts and securing a sustainable future.