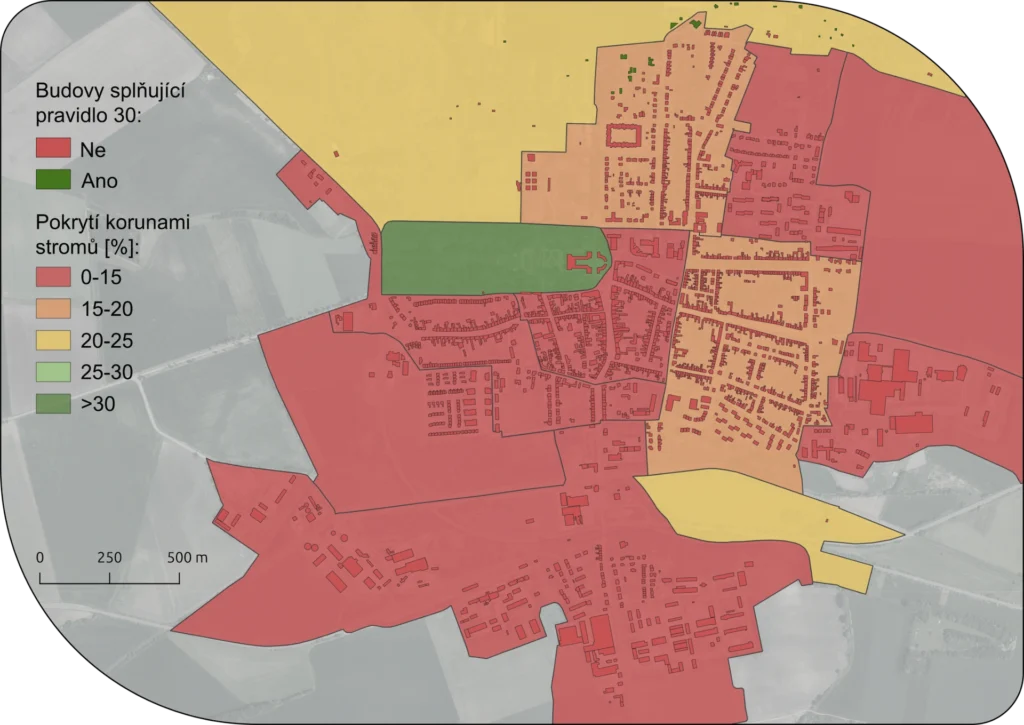
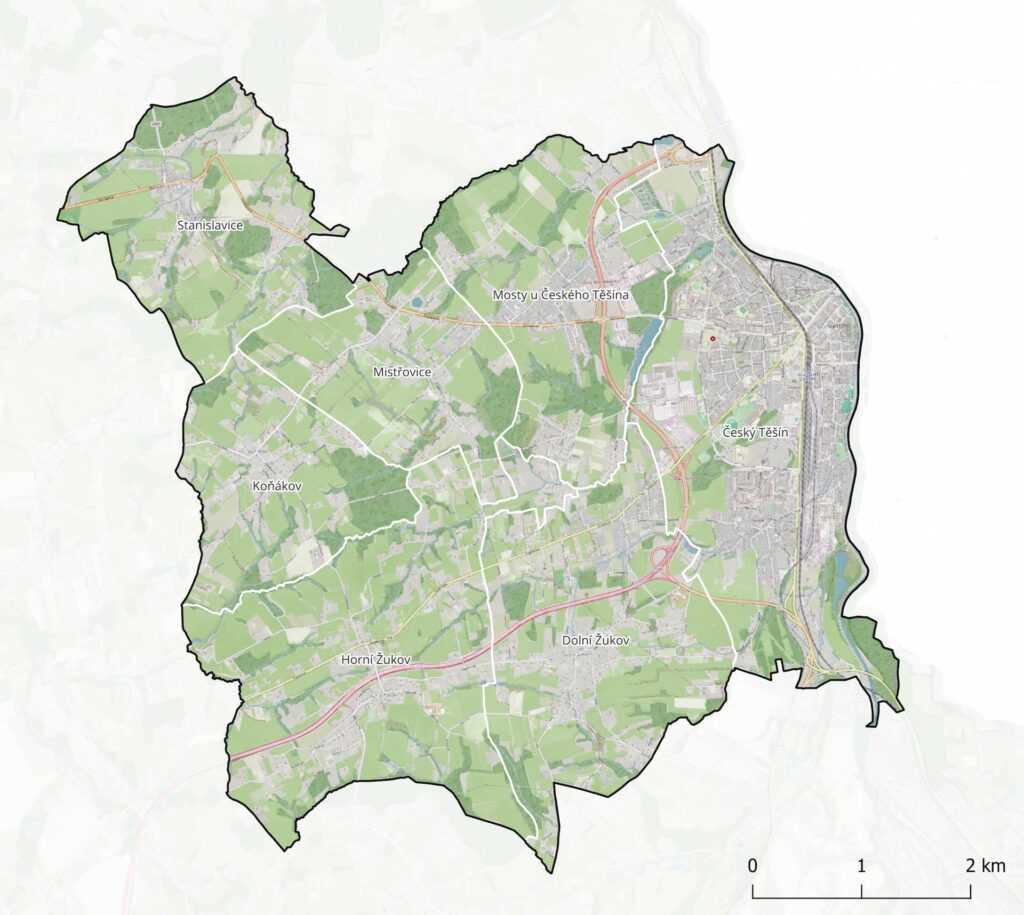
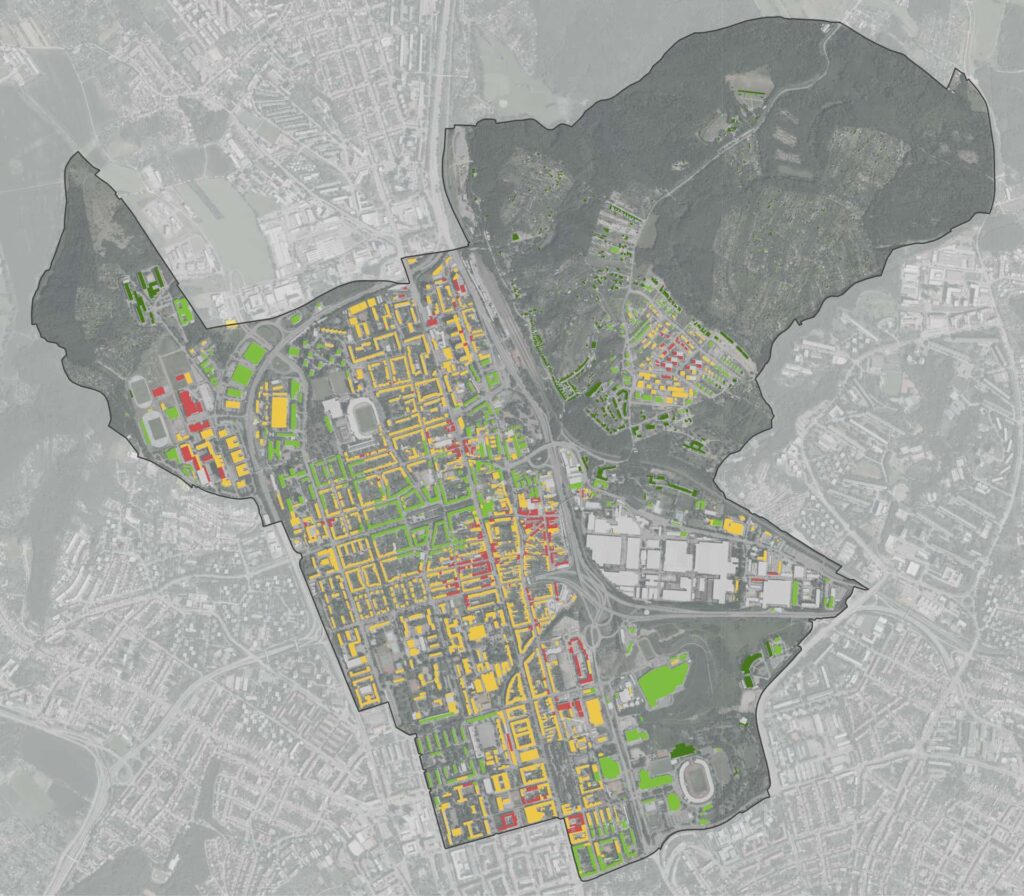
Combined heat and power (CHP), also known as cogeneration, is a way to use the energy contained in fuel with maximum efficiency. It can be applied wherever there is a need to produce heat. A cogeneration unit is based on the principle of a thermal (usually gas) power plant. However, it is designed to minimize heat losses, and all the energy that remains in the steam circuit after passing through the generator is used for heat supply. Compared to a standalone power plant, this saves heat that would otherwise escape as waste.
Cogeneration also has significant applications in processes where a large amount of waste heat is generated in the production of other products. This can include chemical operations involving highly exothermic reactions, operations involving working with metals at high temperatures, etc. Cogeneration can also be used in the largest facilities. An example might be the use of waste heat from a nuclear power plant to supply heat to a city.