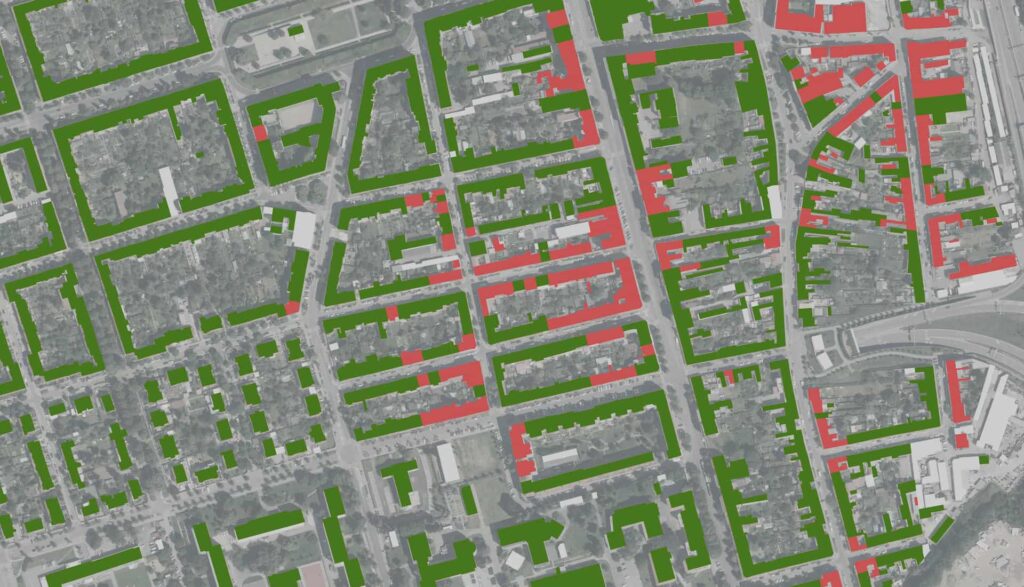
LCA, which stands for Life Cycle Assessment, is a broad methodology used to assess the overall environmental impacts of products or services over their complete life cycle. This process starts with the extraction and processing of raw materials, continues through the production, distribution and use of the product, and ends with its recycling or disposal. LCA aims to identify the phases where the greatest environmental burden occurs and thus provide the basis for effective improvements in environmental sustainability.
LCA steps:
- Definition of objectives and scope: This step involves establishing the purpose of the study, defining the product or system being evaluated, and defining its functional boundaries.
- Life Cycle Inventory (LCI): Collecting data on all inputs (e.g. energy, water, raw materials) and outputs (air, water and soil emissions, waste) associated with each phase of the product life cycle.
- Life Cycle Impact Assessment (LCIA): Analysis of the data collected to quantify environmental impacts such as global warming, ozone layer, acid rain, eutrophication, smog, toxic health effects, etc.
- Interpretation of results: evaluation and discussion of the impacts identified, identification of areas with the biggest potential for improvement and recommendations for reducing environmental impact.
LCA is a widely accepted and recommended tool for ensuring objectivity in environmental assessments.
With its ability to provide detailed and quantitative information on environmental impacts, LCA helps companies, regulators and consumers make more informed decisions that lead to more sustainable practices. This not only improves a company’s image in the marketplace but can also lead to